Connective Tissue
Overview Of Connective Tissue Matrix, Types Of Connective Tissue, Connective Tissue Composed Of Ground Substance And Protein FibersGeneral structure of connective tissue, Mostly fluid connective tissue
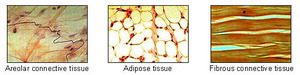
Connective tissue is found throughout the body and includes fat, cartilage, bone, and blood. The main functions of the different types of connective tissue include providing support, filling in spaces between organs, protecting organs, and aiding in the transport of materials around the body.
Connective tissue is composed of living cells and protein fibers suspended in a gel-like material called matrix. Depending on the type of connective tissue, the fibers are either collagen fibers, reticular fibers, or elastin fibers or a combination of two or more types. The type and arrangement of the fibers gives each type of connective tissue its particular properties.
Blood is a liquid connective tissue composed of a fluid matrix and blood cells. The blood cells include white blood cells, which function in the immune system, and red blood cells, which transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. The fluid part of the blood (the plasma) transports hormones, nutrients, and waste products, and plays a role in temperature regulation.
See also Skeletal system.
Resources
Periodicals
Brittberg, Mats, et al. "Treatment of Deep Cartilage Defects in the Knee with Autologous Chondrocyte Transplantation." New England Journal of Medicine 331 (October 1994).
Couzens, Gerald Seor, and Paula Derrow. "Weak in the Knees: New Ways to Protect—and Prevent—this Fragile Joint." American Health 12 (June 1993): 70.
Larkin, Marilynn. "Coping with Connective Tissue Diseases." FDA Consumer 26 (November 1992): 28.
Urry, Dan W. "Elastic Biomolecular Machines: Synthetic Chains of Amino Acids, Patterned After Those in Connective Tissue, Can Transform Heat and Chemical Energy Into Motion." Scientific American 272 (January 1995): 64.
Kathleen Scogna
Additional topics
- Connective Tissue - Overview Of Connective Tissue Matrix
- Connective Tissue - Types Of Connective Tissue
- Connective Tissue - Connective Tissue Composed Of Ground Substance And Protein Fibers
- Other Free Encyclopedias
Science EncyclopediaScience & Philosophy: Condensation to Cosh