TYPES OF ROCKS
Igneous Rocks, Sedimentary Rocks, Metamorphic Rock
We all know a rock when we see one. But what makes something a rock? By definition, a rock is a mass of mineral matter.
A mineral is a naturally occurring crystalline substance. There are thousands of different types of minerals. Some minerals you may know include salt, coal, copper, quartz, and talc.
 A quartz cluster.
A quartz cluster.
Think of rocks as a meal, and the minerals as the ingredients that make up the meal. There are thousands of different ingredients, and different combinations of those ingredients make different meals. In the same way, each rock has its own “ingredient list” of minerals.
All the thousands of different rocks fall into one of three categories: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
 Hot magma river.
Hot magma river.
Igneous Rocks
We know that the temperatures inside the Earth are very hot. It is so hot that rocks actually turn into a liquid, called magma. This magma can cool beneath the Earth's crust to form igneous rock.
Magma sometimes erupts from the Earth's surface from a volcano. When magma reaches the surface of the Earth, we call it lava. When lava cools, it forms igneous rock.
Common Igneous Rocks
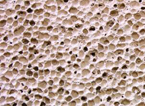 pumice
pumice
 obsidian
obsidian
 granite
granite
 basalt
basalt
Common Sedimentary Rocks
 limestone
limestone
 shale
shale
 sandstone
sandstone
 gypsum
gypsum
 Layers of sedimentary rocks.
Layers of sedimentary rocks.
Sedimentary Rocks
Over time, even something as hard as rock will begin to wear away. When rock wears down, it breaks into much smaller pieces, called sediment.
The small pieces of sediment collect together in layers called sediment beds. As the beds get larger, the pressure squeezes the sediment together to form new rock.
Sedimentary rock is new rock formed from the sediment of older rocks.
Metamorphic Rock
A caterpillar changing into a butterfly is an example of metamorphosis. Metamorphosis means to change from one thing into another. Metamorphic rock is rock that has changed from one type of rock to another by pressure or heat. For example, after thousands of years of pressure and heat, limestone is changed into marble.
Metamorphic rocks can be formed from igneous, sedimentary, or even other metamorphic rocks.
 Coal can change to a diamond.
Coal can change to a diamond.
Common Metamorphic Rocks
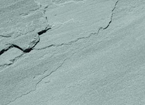 slate
slate
 marble
marble
 quartzite
quartzite
 soapstone
soapstone
Additional topics
- LAND FORMATION - Constructive Forces, Folding, Faults, Magnitude and Effect, Volcanic Eruptions, Deposition of Sediment, Destructive Forces, Weathering, Erosion
- PLATE TECTONICS
- Other Free Encyclopedias