CONSUMERS
Secondary Consumers, Tertiary Consumers, Omnivores
Any living thing that needs to eat food is a consumer. All animals are consumers. So are many microscopic creatures.
Many consumers eat plants or parts of plants. They are called primary consumers. They are also known as herbivores. Animals such as cows, horses, elephants, deer, and rabbits are grazers. They eat grass and the leaves from bushes and trees.
 Hummingbirds need lots of energy to keep themselves alive. Sugary nectar is a high-energy food that keeps them going.
Hummingbirds need lots of energy to keep themselves alive. Sugary nectar is a high-energy food that keeps them going.
OCEAN HERBIVORES
 The ocean has many herbivores. Many of these primary consumers feed on phytoplankton. One group is zooplankton. Zooplankton are animal plankton. Other herbivores include small fish, squid, sea urchins, and krill. The shrimplike krill are found in the cold oceans. And sea urchins, as you know, feed on coral reefs and kelp.
The ocean has many herbivores. Many of these primary consumers feed on phytoplankton. One group is zooplankton. Zooplankton are animal plankton. Other herbivores include small fish, squid, sea urchins, and krill. The shrimplike krill are found in the cold oceans. And sea urchins, as you know, feed on coral reefs and kelp.
Other animals eat seeds and fruit. Among these are squirrels, bats, sparrows, finches, and parrots. Hummingbirds, butterflies, and bees eat the nectar from flowers. Soil animals, such as grubs and worms eat plant roots. All these animals are primary consumers.
Secondary Consumers
Next come the secondary consumers. These animals eat primary consumers. Some of these are large predators such as lions, wolves, crocodiles, and eagles. They may eat animals bigger than they are. Some lions, for example, kill and eat water buffalo. The buffalo weigh twice as much as the lions do.
 Weasels catch very large prey. They are deadly killers. A single bite to the back of a rabbit's neck kills it at once.
Weasels catch very large prey. They are deadly killers. A single bite to the back of a rabbit's neck kills it at once.
FIERCEST PREDATOR?
Which animal is the fiercest predator? You could measure the fierceness of a predator by the size of its prey. Then weasels would top the list. Weasels often hunt rabbits. Rabbits can weigh nearly ten times as much as the weasel.
Other secondary consumers eat animals smaller than they are. Shrews, moles, birds, and most lizards eat insects. Some larger animals also eat insects. Anteaters and sun bears are two examples. These animals have to eat many insects. An anteater, for instance, may eat as many as 30,000 insects every day.
 Mantises are also fierce predators. They eat all kinds of small creatures, including spiders, like this one.
Mantises are also fierce predators. They eat all kinds of small creatures, including spiders, like this one.
Tertiary Consumers
Some animals are called tertiary consumers. This means they eat secondary consumers. Tertiary consumers are often the “top predators” in a food chain. This means that no other animals eat them.
 A great white shark leaps out of the water, catching a seal in its jaws. A shark is a tertiary consumer.
A great white shark leaps out of the water, catching a seal in its jaws. A shark is a tertiary consumer.
An area has only a few top predators. To see why, think about the energy pyramid. (See page 10). It has many plants at the bottom. But only some of the energy from those plants gets turned into new animals. This means there will be fewer primary consumers. And there will be even fewer secondary and tertiary consumers.
LONG FOOD CHAINS
In the ocean, food chains can be long. They may have a stage beyond tertiary consumers. For example, plant plankton is eaten by animal plankton. These creatures are then eaten by small fish. The small fish are eaten by a big fish. The big fish could then be eaten by a shark or a whale.
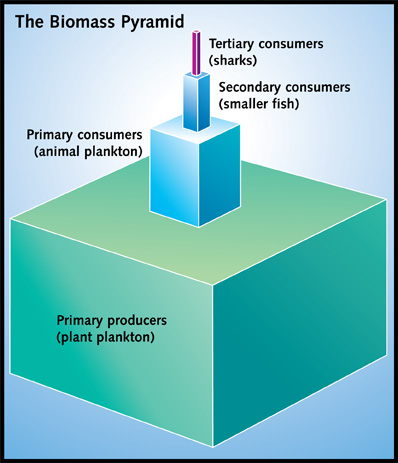 This biomass pyramid is very similar to the energy pyramid on page 10. A habitat can support many more plants than primary or secondary consumers.
This biomass pyramid is very similar to the energy pyramid on page 10. A habitat can support many more plants than primary or secondary consumers.
 Bears, like this grizzly, enjoy catching salmon or other fish. However, they also eat plant food such as fruit and honey.
Bears, like this grizzly, enjoy catching salmon or other fish. However, they also eat plant food such as fruit and honey.
Omnivores
Most humans are not just primary consumers or just secondary consumers. We eat both plant food and animal food. We are omnivores.
Other animals are omnivores, too. Foxes, for instance, eat other animals. But they also eat fruit. Bears, raccoons, seagulls, and cockroaches are also omnivores.
Some omnivores are scavengers. This means they eat food that other animals have left. Hyenas, for example, eat the remains of animals that have been killed by predators. They have strong jaws and teeth. With them, they can crunch through bones.
 Hedgehogs eat mainly slugs, snails, beetles, and worms, but they also eat fruit.
Hedgehogs eat mainly slugs, snails, beetles, and worms, but they also eat fruit.
PARASITES
Parasites are animals or plants that live on or inside other animals or plants. They are consumers. The mistletoe plant is a parasite. It lives on other plants. Roundworms are also plant parasites. Fleas and tapeworms are also parasites. They sometimes feed on humans.
Additional topics
- DECOMPOSERS - Big Decomposers, OCEAN CLEANERS, Little Decomposers
- PRODUCERS - Producers in the Oceans, Kinds of Plant Plankton
- Other Free Encyclopedias