What are Wetlands?
Wetlands are ecosystems where water covers the soil, or is near the surface of the soil, for most or all of the year. You can find wetlands on every continent except Antarctica, from the tundra to the tropics.
 Wetlands provide a habitat for a wide variety of plants and animals.
Wetlands provide a habitat for a wide variety of plants and animals.
 On North Carolina's Outer Banks, coastal marshes are home to waterfowl, fish, birds, mammals, and amphibians.
On North Carolina's Outer Banks, coastal marshes are home to waterfowl, fish, birds, mammals, and amphibians.
There are two general types of wetlands: coastal, sometimes called tidal, and inland. We find coastal wetlands near the ocean, where saltwater mixes with fresh water to form varying degrees of brackish water. In coastal wetlands, the water levels vary throughout the day due to the changing tides.
Few plants grow well under these conditions, so many shallow coastal wetlands are barren mud flats or sand flats. However, in some wetlands we can find grasses or mangroves that have adapted to the salty water.
Inland wetlands contain fresh water. They may be found along rivers and streams, near lakes and ponds, or off by themselves, surrounded by dry land.
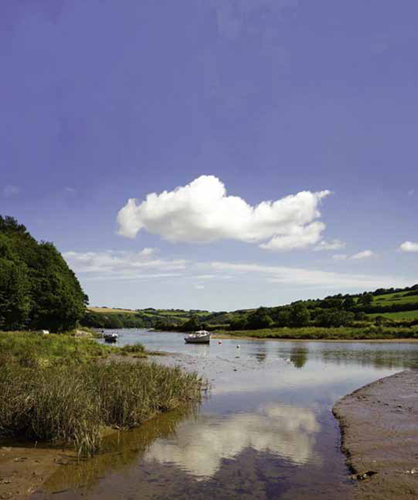 In England, grasses growing along an estuary help small animals hide from their predators.
In England, grasses growing along an estuary help small animals hide from their predators.
Permanent wetlands contain water year round, while seasonal wetlands are wet 6 months or less. Temporary wetlands contain water for only 30 days or less each year.
 Wetlands in Colorado's Gunnison National Forest provide food and water to migratory birds.
Wetlands in Colorado's Gunnison National Forest provide food and water to migratory birds.